Introduction
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) are one of the concepts associated with Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs). PTAs emerged in the first globalization wave in the 19th century. The German Customs Union (Zollverein), established by Prussia in 1833, which had the goal of a common tariff and trade policy, is an example of early economic integration.1 The Cobden-Chevalier trade agreement, signed between Britain and France in 1860, is another example of a PTA.2 The best known are the German monetary union, Latin monetary union, and Scandinavian monetary union.3 The post-war period in 1945 started the second globalization wave when significant developments in terms of economic integration took place.4 One of the most important of these is the European Economic Community (EEC) established by six European countries through the Treaty of Rome, in 1957.5 The third wave of globalization beginning in 1980 was the time when many developing countries liberalized their trade policy resulting in a further increase in the number of trade agreements.6
Turkey is among the countries that liberalized their foreign trade in the 1980s. However, its regional integration initiative began in 1963 under the Ankara Agreement with the EEC. Although Turkey still has not become a full member of the European Union, it has continued its efforts to integrate with the world economy through its FTAs signed with several countries since 1990, the most recent example being the FTA signed with the United Kingdom (UK) in 2021.
In this study, the FTA signed with the UK is examined in the context of economic diplomacy, and bearing in mind that bilateral trade agreements are a tool in economic diplomacy, the concept of economic diplomacy is firstly analyzed. The experience of Turkey’s free trade agreement is then discussed. Bilateral economic relations between Turkey and the UK are addressed and details of the agreement are examined. Finally, in terms of economic diplomacy, suggestions for further co-operation between the two countries have been made.
The Concept of Economic Diplomacy
Economic diplomacy is mainly about foreign economic relations and achieving economic goals. In this context, economic diplomacy is defined as the trade in goods and services and as the influence of the state on foreign economic relations, with regard to the flow of production factors (labor, capital, technology, and natural resources) between the domestic and international. Generally speaking, in economic diplomacy, the aim is to improve private political relations with various countries, to ensure the security of the country through membership in various international organizations, and to shape the state’s image in the world.7
These goals, namely securing the country and shaping the state’s image in the world, are all about results-oriented approaches. In addition, there are also views that assess economic diplomacy in terms of the decision-making processes, rather than structural factors. In this context, analyzes are carried out on the basis of international economic issues.8
The increase in the degree of openness of economies to the outside has also increased the likelihood of external factors affecting a country’s economy
Economic diplomacy is a host of decisions and discussions on international economic issues. It has become an important working area, with the globalization process and the increase in international economic dependence. It includes the stability of the international financial system, the liberalization of trade, the direction of international investments, and, as a result, global economic problems that affect countries’ achievement of internal political goals.9
Typically, economic diplomacy consists of three elements listed as follows:
(i) The first element of economic diplomacy is the use of political relations in order to increase economic profit and reduce damage. In this context, the search for political support is made to increase international trade and investments, fight market failures, and reduce the risks of cross-border trade.
(ii) Economic relations and assets can be used for the stability of political relations. This is an example of increasing economic security. For this, it is possible to implement structural policies, bilateral trade, and investment agreements.
(iii) To achieve these objectives, it must be ensured that the appropriate political and international economic environment is established. Multilateral negotiations and supranational organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and the EU contribute to the creation of this environment.10
The goals of economic diplomacy can be said to be related to the globalization process, because the development of international trade in goods and services, the acceleration of capital flows, and the spread of labor flows have allowed the bonds between the countries to be arbitrated. It can be stated that globalization provides significant welfare gains in this regard. On the other hand, there are some negative aspects to this process. The increase in the degree of openness of economies to the outside has also increased the likelihood of external factors affecting a country’s economy. In other words, the globalization process has made the countries’ economies open to external pressure which has led to increased problems related to economic security. In this context, economic diplomacy is committed to improving welfare gains and reducing the threats to economic security.11
There are some economic diplomacy tools used for the purpose of implementing the stated objectives. These tools are shown in Table 1; where economic diplomacy is divided into positive and negative instruments. Positive economic diplomacy instruments focus on exports and encourage bilateral investments. To this goal, government visits, diplomatic representations, and economic diplomats are used to promote trade. Negative economic diplomacy is the opposite of these practices, in other words, the aim is to be achieved by placing various obstacles in front of trade. These obstacles include various economic embargoes and sanctions, as well as the termination of membership in international organizations.
Table 1: Tools of Economic Diplomacy
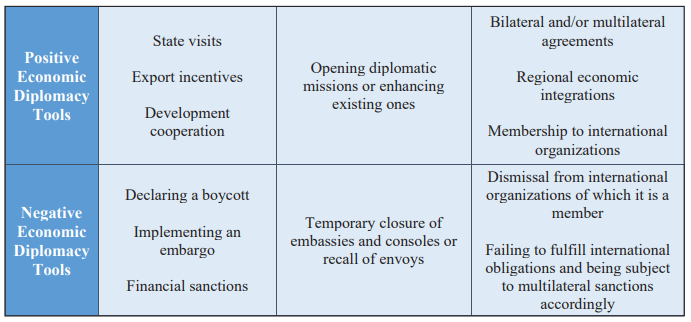 Source: Peter A.G. van Bergeijk, et al.12
Source: Peter A.G. van Bergeijk, et al.12
Proactive Economic Diplomacy Strategy of Turkey
In the literature, a very restricted number of studies deal with Turkey’s economic diplomacy. Öğütçü and Saner discussed Turkey’s economic diplomacy from the perspective of EU membership and examined the gains Turkey could achieve with membership through proactive economic diplomacy.13 In another study, Öğütçü considered Turkey’s novel economic diplomacy strategy as an essential part of Turkey’s wide range of policy and institutional reform under the framework of ‘more economics and less geopolitics.’14 Paolo examined Turkey’s increasing activity in Africa in the context of soft power instruments, development aid, and humanitarian assistance, establishing a relationship between economic diplomacy and religious factors.15 In view of the changes in the structure of the international system, Ünal examined Turkey’s economic diplomacy in the context of developments related to Turkey’s political economy by focusing on the activities of the Foreign Economic Relations Board (DEİK), which as the global horizon of the Turkish business world.16 Ünay assesses Turkish foreign policy in terms of international political economy in the context of neoliberal reforms in the 1980s and 2000s and examines the ascendancy of economic issues to the level of high-politics within the framework of economic globalization.17 Vallée mentions that economic and financial matters have been an essential pillar of Turkey’s diplomacy, he suggests that the opening of new markets for its goods and the protection of financing for its investments has become a central foreign policy input.18 Yamak and Saygın suggest that the Turkey Wealth Fund (TWF) should not be seen as merely a tool of economic policy, but rather TWF should be considered as an economic diplomacy instrument.19 Some studies explain Turkish foreign economic policy with the concept of ‘trading state.’ The nature of the trade state is described as follows: “…a broader range of players are invited to participate in foreign policy-making or diplomatic games, and their interests and goals differ significantly from those of Turkey’s conventional foreign policy-makers.”20 Rosecrans used this term as “releasing the productive and commercial forces of people and businessmen looking for international marketplaces for their goods.”21 To understand both the Turkish economic diplomacy and the usage of the trading state in this issue, it is necessary to understand the history of Turkey’s proactive economic diplomacy strategy concept.
A broader range of players are invited to participate in foreign policy-making or diplomatic games, and their interests and goals differ significantly from those of Turkey’s conventional foreign policy-makers
Turkey’s proactive economic diplomacy strategy has two main goals: (i) to promote free trade through new economic partnerships; (ii) to build a liberal investment climate to encourage inward Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The content of each goal is evaluated in turn below.
Economic and Political Roots of Turkey’s Economic Partnerships Initiatives
Between 1980 and 2001, Turkey had three FTAs in place with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), Israel, and then FYR of Macedonia. The origins of these agreements have been in the economic transformation of Turkey since 1980. The Turkish economy was characterized by centralized planning and inward-looking policies until the Turkish Government declared a major stabilization and liberalization program on January 24, 1980. The key feature of the program was restructuring the Turkish economy from a state-led development model to a liberal export-led one. There were some domestic and external reasons to adopt outward-looking economic policies. Turkey faced serious domestic economic problems before 1980, which were addressed by the measures included in the economic stabilization program adopted in 1980. The import-substitution economic model failed to help the economy and leaving the model was considered as the only way to tackle these problems.22
Some domestic and external actors supported the outward and market-oriented model. Domestic actors such as the military and business groups supported the new economic model because of their own interests. The military did not want to pay for the political instability caused by the economic instability, desiring to preserve the military’s economic and social situation. Business groups were concerned about the distribution policy between 1962 and 1976. The so-called capital owners believed that the government’s policies favoring the masses of workers and peasants, which could be characterized as populist, led to a decline in profitability. The military and capital owners (vested interests), whose interests united at the same point, became a party to the change of the import-substitution economic model.23
Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) significantly improves economic conditions, and it is one of the results of Turkey’s proactive economic diplomacy strategy
Turgut Özal, who served as the 8th President of Turkey, from 1989 to 1993, adopted a foreign policy meant to increase interdependence with neighboring countries. The founding of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation Organization (BSEC) efforts to reduce conflict between Greece and Turkey, the construction of a water pipeline from Turkey to the Gulf and Israel, conducting state visits with business delegations to ease Turkey’s access to export markets, and eliminating visa requirements for Greek citizens are the results of such an understanding.24
Turkey had a very fragile banking system before 2001, which came to light when Turkey experienced a banking crisis in 2000 and 2001. This crisis created opportunities for the Turkish economy, and leaders were aware of the fact that a successful economic diplomacy strategy would require overcoming the fragility of the financial system. Therefore, immediately after the crisis, economic policy initiatives were taken. The Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency (BRSA) announced a comprehensive banking sector restructuring program to strengthen the financial system.25
The second economic initiative was the ‘Transition Program to a Strong Economy’ operationalized in May 2001. The Program aimed at the establishment of macro-economic stability, sustainable growth, structural reforms, and ensuring fiscal discipline.26 The Justice and Development Party (Adalet ve Kalkınma Partisi, AK Party)27 came to power in 2002, following the establishment of these economic initiatives. Since November 2002, the economy has been stabilized, the inflation rate has been gradually decreasing, the integration process with the EU has been accelerated, and accession negotiations with the EU started on October 3, 2005, after adequate compliance with the Copenhagen Criteria. Under the AK Party Administration, Turkish foreign policy has gained a new character, at the heart of which is the transformation from security-focused foreign policy to economic-focused foreign policy. In the post-2001 period, via extensive institutional/regulatory reforms, both the restructuring of a ‘regulatory state’ and a positive macroeconomic climate characterized by strong and sustained growth rates, lower inflation, fiscal discipline, unprecedented levels of FDI inflows, and the completion of large-scale privatization programs have been realized.28
During the reign of the AK Party, growth in foreign trade, and particularly in exports, has accelerated markedly. This increase is one of the outcomes of the new concept in Turkish foreign policy, making it easier for Turkey to establish economic partnerships. Among the most important elements of this policy is Europeanization and aiming for ‘zero problems with the neighbors.’ Europeanization of foreign policy is a means of preserving the government’s domestic and international legitimacy. Zero problems with the neighbors is the creation of a peaceful environment in Turkey through the development of trade and political relations with neighbors.29
As a result of the economic and political initiatives outlined above, the number of economic partnerships established by Turkey and the number of FTAs being signed has increased significantly after 2001. Turkey has signed FTAs with Bosnia-Herzegovina, Palestine, Tunisia, Morocco, Syria (suspended), Egypt, Albania, Georgia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Chile between 2002 and 2010. These countries are mainly located in the Middle East, Balkan region, and Africa but also include Turkey’s neighbors. Turkey has signed FTAs with Mauritius, South Korea, Malaysia, Moldova, Faroe Islands, Singapore, Kosovo, Venezuela, and the UK after 2010, none of which are close neighbors.30
Invest in Turkey
Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) significantly improves economic conditions, and it is one of the results of Turkey’s proactive economic diplomacy strategy. There are many reasons to invest in Turkey such as; economic growth, large domestic and regional markets, strategic location, demographic factors, labor force situation, economic, and political reforms, and building an available investment climate are the main reasons to attract inward FDI to Turkey. Turkish economy grew by 4 percent per year on average between 2001 and 2010. This is almost the same growth rate with emerging and developing European countries (3.9 percent). Between 2011 and 2018 Turkish economy grew by 6.1 percent per year on average exceeding many emerging and developing European countries. In this period the highest growth rate was realized in 2011 (11.1 percent) and the lowest growth rate was recorded in 2018 (2.6 percent). In terms of real GDP growth, it is understood that Turkey performed well. When the real GDP growth index was adopted as 100 in 2002, Turkey achieved higher real GDP growth than Czechia, Hungary, Bulgaria, Poland, and Romania in 2002-2007. Turkey’s real GDP growth fell behind Romania, Bulgaria, and Poland in 2008-2009; however, once more it reached higher real growth rates than the same countries in 2010-2018.31
The key goals of the incentive scheme are to increase production and jobs, direct investments to large-scale projects, minimize regional growth disparities, and reduce reliance on the import of intermediate goods
In addition to growth rates, Turkey is a country with fiscal discipline in terms of appropriate investment conditions. Fiscal discipline is a key measure for investors in terms of a country’s ability to make borrowing costs and future payments. Turkey had higher government debt to GDP rates than the EU between 2000 and 2008; however, Turkey managed to sharply reduce government debt to GDP rate from over 70 percent in 2000 to about 30 percent in 2018. Turkey’s government debt to GDP rate is about 30 percent less than that of the EU in 2018.32 One of the key positive outcomes of fiscal discipline is budget balance. Turkey had a higher budget deficit than the EU in 2001-2002. The positive impact of fiscal discipline has been expressed in a notably reduced shortfall in Turkey’s budget balance. Turkey had a lower budget deficit than the EU between 2003 and 2017 and has sharply reduced the budget deficit from over 30 percent in 2001 to about three percent in 2019.33
The results of Turkey’s efforts to improve the investment climate have had an impact on exports of goods. For the first time in the history of the Republic of Turkey, Turkey’s export volume, with major accomplishments and government stimulus, is at its highest point. The country earned $168.1 billion from exports in 2018, and it increased 7.1 percent with $11.1 billion compared to 2017. While imports are still higher in Turkey, exports have increased in volume, while import volumes have decreased by 4.6 percent to $223.1 billion in 2018. $84.1 billion, equivalent to 50 percent, of exports, was made to Europe in 2018, with Germany, the UK, and Italy being Turkey’s top three export countries. In 2018 exports to Africa also grew by 24 percent, while Latin American countries exported more goods, with a rise of 35.6 percent from 2017. Exports to Mexico and India, which Turkey identified as target countries, also grew in volume, increasing from 2017 to 2018 by 36 and 48 percent, respectively. However, projections show that 50 percent of the country’s goods will continue to be exported to EU countries, making it Turkey’s main market. For the most part, Turkey’s exports are from the automotive, agriculture and food, ready-made clothing, textile, and iron-steel industries.34
Turkey provides a lot of opportunities for international investors with the country’s low operating costs, local producers, virgin markets, and strong consumer spending. There are also other advantages, such as the ability to avoid double taxation (if you are a foreign investor in Turkey you only pay taxes in Turkey, not in your home country), the right to freely move your earnings in Turkey to abroad, and the right to acquire Turkish citizenship, (if you have made $500 thousand fixed capital investment in Turkey you have the right to acquire Turkish citizenship). A new scheme of investment incentives that has been in place since January 1, 2012, aimed at boosting growth in Turkey. The key goals of the incentive scheme are to increase production and jobs, direct investments to large-scale projects, minimize regional growth disparities, and reduce reliance on the import of intermediate goods. Five separate schemes compose the framework of investment incentives: general, regional, priority, large-scale, and strategic investment incentives schemes.35 In connection with the subject matter of this study, Turkey’s experience of bilateral agreements or FTAs, one of the economic diplomacy tools, will be examined in the next topic.
The History and Development of Turkey’s FTAs
Today, many countries have begun to choose bilateral and/or regional FTAs. This is largely due to the WTO’s successful liberalization policy. Although WTO regulations are not considered sufficient today, about 400 FTAs have currently been reached. Turkey, a member of GATT and WTO, has also been establishing FTAs for nearly 30 years and as a member of the Customs Union, Turkey is striving to implement the new generation of FTAs in line with the EU. Turkey already has 21 FTAs in forces in place. The countries/country blocs in which Turkey has signed FTAs are as follows: EFTA, Israel, North Macedonia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Palestine, Tunisia, Morocco, Syria, Egypt, Albania, Georgia, Montenegro, Serbia, Chile, Mauritius, Malaysia, Moldova, the Faroe Islands, South Korea, Singapore, and the UK.36 Table 2 demonstrates the dates when these FTAs were signed and when they came into force.
Table 2: Turkey and Its FTAs
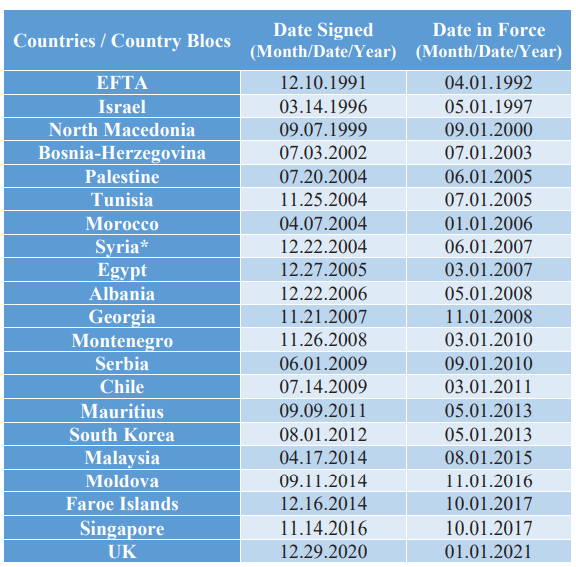 * Suspended on December 6, 2011
* Suspended on December 6, 2011
Source: Republic of Turkey Ministry of Trade37
While efforts are in progress to extend the scope of existing FTAs, there are new agreements for which the ratification process is underway. Negotiations on FTAs have started with countries including Japan, Ukraine, Indonesia, Mexico, Thailand, and Pakistan. In addition, FTAs are planned with countries such as the U.S., Canada, and India.38
Process Leading to an FTA and Economic Relations between Turkey and the UK
Due to the bilateral economic and political relations that have developed between Turkey and the UK in recent years, their FTA has been selected as an example to understand Turkey’s proactive economic diplomacy strategy. Turkey and the U.K. have strengthened their bilateral relations, but their relations with the EU have deteriorated. Before analyzing the details of the FTA between Turkey and the U.K., the factors that have led to the deterioration of the two countries’ relations with the EU, will be briefly summarized. This will also explain why the FTA between Turkey and the U.K. was chosen to focus on in this study.
Turkey and the U.K. have strengthened their bilateral relations, but their relations with the EU have deteriorated
The UK, which joined the European Economic Community, established in 1957 by six European countries, decided to leave the alliance after 43 years as a member state. This was following the result of the referendum on June 23, 2016, when 51.89 percent of UK citizens voted to leave the EU. The term Brexit, comprised of the words British and exit, was coined to indicate the UK’s departure from the EU after this referendum.
The legal basis for any member state’s decision to leave the EU is the Lisbon Treaty, which took effect on December 1, 2009, of which article 50 sets out regulations for the operation of the withdrawal process. The UK began this process on March 29, 2017, with the activation of the Article by Theresa May. The Council of Europe ratified the Withdrawal Agreement on October 17, 2019. On January 31, 2020, the UK left the EU and entered a transition period that ended on December 31, 2020, when the UK formally left the EU single market and customs union.39
With respect to Turkey, its Eastern Mediterranean Policy has caused a strain on Turkey and EU relations and has been declared by the EU as an aggressive policy. Turkey’s natural gas exploration in the Eastern Mediterranean was considered one of the most important factors in the deterioration of relations with the EU.40
Economic relations between Turkey and the UK have been gradually improving in recent years. Table 3 shows the data on bilateral economic relations. UK imports from the world totaled $358.7 billion in 2001, while imports from Turkey only amounted to $2.8 billion; however, by 2019 UK imports from Turkey had increased to $12.1 billion. Over the period 2001-2019, the UK’s total imports from the world increased by about 93 percent, while overall imports from Turkey increased by about 337 percent. In the same period, Turkey’s total exports to the world increased by approximately 446 percent.
Table 3: Comparison of the UK Imports between Turkey and World (2001-2019, $ Thousand)
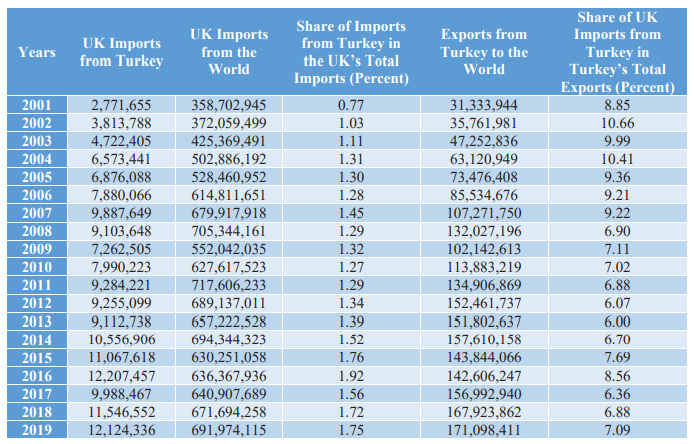 Source: International Trade Centre (2020)41
Source: International Trade Centre (2020)41
Figure 1 shows the total trade volume between Turkey and the UK over the period 1999-2019. Trade volume between the two countries, which was £3.8 billion in 1999 increased to more than double and reached £7.9 billion in 2005. As a result of steady increases from 2005 to 2008, it was £9.9 billion in 2008. Due to the global economic crisis, it briefly dropped to £9.7 billion in 2009 but in the following 10 years, it continued increasing steadily to reach £18.6 billion by 2019.
Figure 1: Total Trade between Turkey and the UK (1992-2019, £ Million)
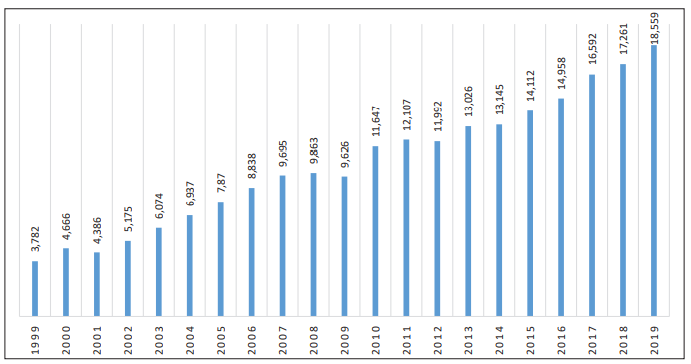 Source: Office for National Statistics(2020)42
Source: Office for National Statistics(2020)42
Within these figures, there are trade deficits, the sources of which can be seen in Table 4. Figures show the top 5 categories of goods exports and imports between Turkey and the UK in 2019. From them, it can be seen that the UK had advantages in ‘machinery and mechanical appliances’ and ‘precious stones and metals.’ However, Turkey had advantages in ‘vehicles other than railway or tramway stock’ and ‘electrical machinery and equipment.’ Turkey’s overall advantage was higher than the UK as it exported £5.9 billion in goods to the UK and imported £3.5 billion in goods from the UK. ‘Vehicles other than railway or tramway stock’ was the largest category of goods exported to the UK, valued at £1.9 billion, with ‘machinery and mechanical appliances’ goods following as the second-largest export (£1 billion). ‘Machinery and mechanical appliances’ was also the largest category of goods imported from the UK, valued at £1.5 billion, with other precious stones and metals following as the second-largest import (£937 million).
Table 4: Top 5 Goods Trade between Turkey and the UK in 2019 (at HS23 level, £ million)
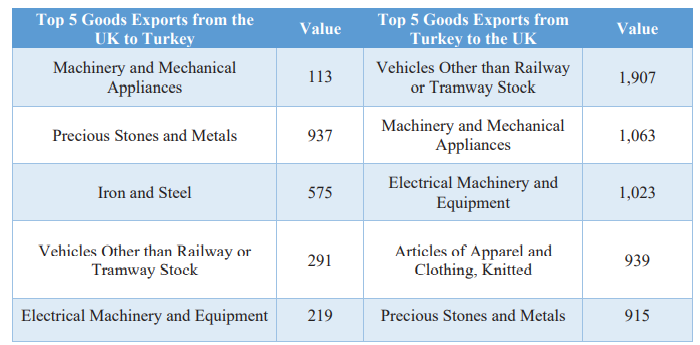
Source: Department for International Trade43
Table 5: Top 5 Services Trade Between Turkey and the UK in 2019 (£ million)
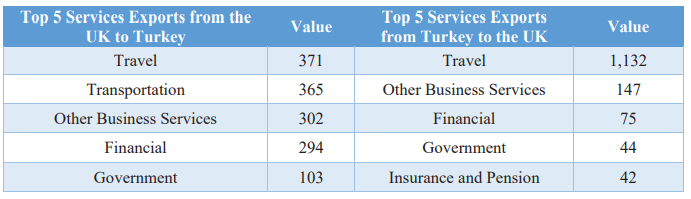
Source: Department for International Trade44
Table 5 shows that the top services exported to the UK were travel (£1.1 billion) and other business services (£147 million) in 2019. Turkey’s top services imported from the UK were travel (£371 million) and transportation (£365 million). While Turkey had a greater advantage in travel services, the UK had advantages in business, financial, and government services.
The arbitration panel, which is envisioned to be established within six months of Turkey’s current arrangement with the EU, has been reduced to two months by agreement
Figure 2 shows the share of foreign direct investment inflows to Turkey by countries between 2003 and 2019. The Netherlands ranks first with a share of 16.1 percent followed by the U.S. (7.6 percent), the Gulf, and the UK (both at 7.0 percent). However, looking at 2019 alone, the UK with (14.9 percent) ranks second after the Netherlands (19.9 percent).45
Figure 2: FDI Inflows to Turkey by Country
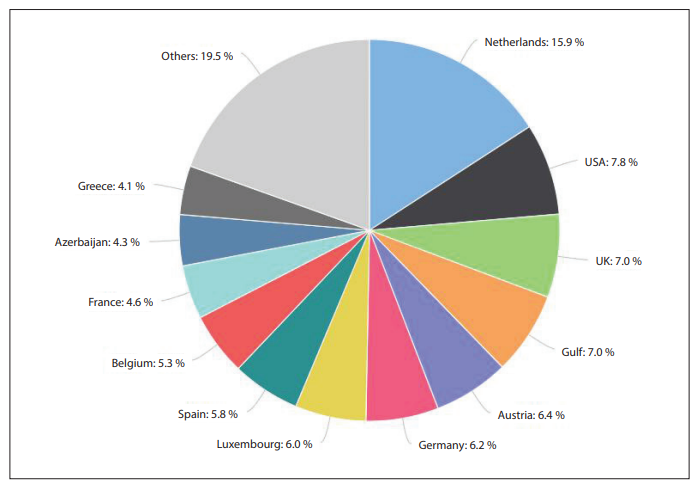
Source: The Investment Office of the Presidency of the Republic of Turkey46
Details of FTA between Turkey and the UK
Turkey-UK trade relations were carried out in the framework of the EU-Turkey Customs Union before Brexit. The trade deal signed after Brexit changed these relations and ensured that trade rules are conducted independently from the Customs Union. The FTA introduced some enhancements to trade in goods, customs, and trade facilitation, technical barriers to trade, competition, and dispute settlement. These enhancements are summarized below.47
Before the UK left the EU, the trade in goods between Turkey and the EU was in line with the Customs Union rules. These rules regulate the free movement of goods between Turkey and the EU. All goods covered by free circulation are exported free of duty to the other country, regardless of where they have been manufactured. The agreement between Turkey and the UK has transitioned the Customs Union into a traditional FTA. This means that goods must be produced at one of the parties in order to be treated without import duties. One of the enhancements made by the agreement is the converted tariff commitments from Euro to Sterling. The second amendment is the elimination of agricultural tariffs in order to avoid disrupting Turkish exports of agricultural products. Thirdly, a single tariff plan has been agreed upon to replace several tariff programs in trade between the two countries. The Tariff Rate Quotas have also been modified. The quotas have been resized to prevent damage to the traders of the two countries and to ensure continued trade. The change in the Rules of Origin is that EU materials can be recognized in exports between the two countries. For this purpose, the temporary Rules of Origin Protocol has been added to the Agreement. The arrangement of Customs and Trade Facilitation on the Agreement is the acceptance of the Mutual Administrative Assistance Protocol in Customs matters. The protocol provides a legal basis for sharing information between the two countries and strengthening bilateral relations. The Agreement couldn’t regulate the technical barriers to trade to the extent required. Since Turkey’s current agreement with the EU is an obstacle a clause has been added to the Agreement to overcome the obstacle. The clause guarantees that some updates will be made about technical barriers to trade in the future. The Agreement contains a clause regulating competition rules between the two countries. This means that competition rules are committed to being transparent and fair. These rules are to be applied equally for the public and private enterprises of both countries. The agreement has made many changes in dispute settlement. The arbitration panel, which is envisioned to be established within six months of Turkey’s current arrangement with the EU, has been reduced to two months by agreement. According to the article in the agreement, it has been decided to establish a review mechanism to determine progress in compliance with the arbitration award. In the event of non-compliance, a mechanism has been added to encourage the complaining party to meet the obligations of the agreement and to encourage the other party to come into compliance.
The UK’s secession from the EU has led to the need for a new agreement to continue trade between Turkey and the UK
Discussion and Conclusion
This study is based on the fact that bilateral trade agreements are an instrument of economic diplomacy. In general, economic diplomacy covers strategies about domestic companies’ access to international markets and attracting foreign direct investments. FTAs are being used effectively to implement these strategies today. Economic and political reasons for FTAs bring about the active use of economic diplomacy. The example provided in this study is the FTA which Turkey has signed with the UK. In the past twenty years, Turkey has continued its effort to integrate into the world economy through FTAs, and thanks to these agreements, it has improved its trade volume. Turkey continues to hold trade negotiations and aims to implement trade agreements under approval.
One aspect of the trade agreement between the two countries is their relations with the EU. The Brexit process has caused damage to the UK-EU relations over time. The UK’s current problems with the EU have become apparent in this process. With the completion of this process, it means that the UK will follow an independent trade policy from the EU in the coming years. This has enabled the UK to have new trade agreements. On the other hand, Turkey-EU relations have also deteriorated in recent years. One of the most important reasons for this deterioration is Turkey’s Eastern Mediterranean policy. Turkey’s continuation of gas exploration activities in the Eastern Mediterranean means a conflict of interest with the EU. There are some serious problems with this policy, especially with France and Greece.
Problems with the EU have been an opportunity for both countries. When viewed in terms of economic diplomacy, it shows that improving bilateral economic relations is appropriate for the interests of both countries. The increase in economic relations between the two countries in the Brexit process has created a good basis for this. The UK’s secession from the EU has led to the need for a new agreement to continue trade between Turkey and the UK. Both countries, which were aware of this and wanted to avoid damaging their trade relations, had already started negotiations for a new trade agreement. They have successfully completed this process with a new trade agreement that took effect on January 1, 2021.
This trade agreement introduces some new regulations in trade between the two countries. These regulations are designed to protect the economic interests of both countries. The role of economic diplomacy was highlighted in these negotiations. The effective use of economic diplomacy of the two countries has played an important role in the processes of a successful conclusion Changes have been made regarding goods, customs, and trade facilitation, technical barriers to trade, competition, and dispute settlement with the new trade agreement. Such changes are expected to drive trade between the two countries in the coming years.
Endnotes
1. Béatrice Dedinger, “Trade Statistics of the Zollverein, 1834-1871,” Cairn, Vol. 140, No. 4 (2015), retrieved August 31, 2021, from https://www.cairn.info/revue-de-l-ofce-2015-4-page-67.htm.
2. A. Iliasu, “The Cobden-Chevalier Commercial Treaty of 1860,” The Historical Journal, Vol. 14, No. 1 (1971), p. 67.
3. Marek Dabrowski, “The Economic and Monetary Union: Past, Present and Future,” Econstor, (2019), retrieved from https://www.econstor.eu/handle/10419/227642.
4. Anne O. Krueger, “Are Preferential Trading Arrangements Trade-Liberalizing or Protectionist?” Journal of Economic Perspectives, 13, No. 4 (1999), p. 106.
5. Larry Neal, The Economics of Europe and the European Union, (UK: Cambridge University Press, 2007), pp. 34-36.
6. “Globalization, Growth, and Poverty: Building an Inclusive World Economy,” World Bank, (2002), retrieved August 31, 2021, from https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/14051?locale-attribute=fr.
7. Maria Ewa Szatlach, “The Importance of Economic Diplomacy in the Era of Globalization (The Case of China),” Repozytorium, (2015), retrieved August 31, 2021, from http://repozytorium.U.K.w.edu.pl/bitstream/handle/item/4200/The%20importance%20of%20economic%20diplomacy%20in%20the%20era%20of%20globalization%20the%20case%20of%20China.pdf?sequence=1.
8. Nicholas Bayne and Stephen Woolcock, “What Is Economic Diplomacy?” in Nicholas Bayne and Stephen Woolcok (eds.), The New Economic Diplomacy: Decision-Making and Negotiation, (UK and U.S.: Ashgate, 2007), p. 1.
9. Stephen Woolcock and Nicholas Bayne, “Economic Diplomacy,” in Andrew Cooper, Jorge Heine, and Ramesh Thakur (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Modern Diplomacy, (UK: Oxford University Press, 2013), p. 385.
10. Peter A.G. Van Bergeijk and Selwyn J.V. Moons, “Economic Diplomacy and Economic Security,” in Carla Guapo Costa (ed.), New Frontiers for Economic Diplomacy, (Instituto Superior de Ciencas Socias e Politicas, 2009), p. 38.
11. Peter A.G. Van Bergeijk, Economic Diplomacy and the Geography of International Trade, (U.S.: Edward Elgar, 2009), pp. 173-174.
12. Peter A.G. van Bergeijk and Selwyn J.V. Moons, “Introduction to the Research Handbook on Economic Diplomacy,” in Peter A.G. van Bergeijk and Selwyn J.V. Moons (Eds.), Research Handbook on Economic Diplomacy: Bilateral Relations in a Context of Geopolitical Change, (UK: Edward Elgar, 2018), p. 3.
13. Mehmet Öğütçü and Raymond Saner, “Fine-Tuning Turkey’s Economic Diplomacy,” Eurasia Critic Magazine, (2008), retrieved August 31, 2021, from http://www.diplomacydialogue.org/publications/economic-diplomacy/80-fine-tuning-turkeys-economic-diplomacy.html.
14. Mehmet Öğütçü, “Turkey’s New Economic Diplomacy: Balancing Commercial Interests with Geopolitical Goals,” Turkish Policy Quarterly, 1 (Spring, 2002), retrieved August 31, 2021, from http://turkishpolicy.com/images/stories/2002-01-futureofTRpolicy/TPQ2002-1-ogutcu.pdf.
15. Alessandro Paolo, “Turkey in Africa: Where Economic Diplomacy Meets Islamic Appeal,” African Studies Centre, (2015), retrieved August 31, 2021, from https://scholarlypublications.universiteitleiden.nl/access/item%3A3144063/view.
16. Uğur Ünal, “Economic Diplomacy of Turkey in The Context of Politics of Prestige in Foreign Economic Relations (A Research on Foreign Economic Relations Board DEIK – Global Horizon of the Turkish Business Community),” Ü. İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Dergisi, Vol. 20, No. 1 (2019), retrieved from https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/cumuiibf/issue/45599/551160, pp. 30-53.
17. Sadık Ünay, “Economic Diplomacy for Competitiveness: Globalization and Turkey’s New Foreign Policy,” Perceptions, Vol. 15, No. 3-4 (Winter 2010), pp. 21-47.
18. Shahin Vallée, “Turkey’s Economic and Financial Diplomacy,” Turkish Policy Quarterly, Vol. 9, No. 4 (Winter 2010), pp. 63-72.
19. Tahsin Yamak and Emre Saygın, “Turkey’s Economic Power Potential: Turkiye Wealth Fund Practiceas an ‘Economic Diplomacy’ Instrument,” Fiscaoeconomia, Vol. 3, No. 1 (2019), pp. 88-114.
20. Kemal Kirişci, “The Transformation of Turkish Foreign Policy: The Rise of the Trading State,” New Perspectives on Turkey, Vol. 40, (2009), p. 33
21. Richard Rosecrance, The Rise of the Virtual State: Wealth and Power in the Coming State, (New York: Basic Books, 1999), p. 27.
22. Zülküf Aydın, The Political Economy of Turkey, (London: Pluto Press, 2005).
23. Korkut Boratav, Türkiye İktisat Tarihi, (Ankara: İmge Kitabevi, 2012).
24. Kirişci, “The Transformation of Turkish Foreign Policy,” pp. 29-57.
25. “From Crisis to Financial Stability (Turkey Experience),” BDDK, (December 29, 2009) retrieved from http://images.mofcom.gov.cn/tr/accessory/201006/1276394632957.PDF.
26. “Merkez Bankası Para Politikası Çerçevesi,” TCMB, retrieved February 10, 2021, from https://www.tcmb.gov.tr/wps/wcm/connect/tr/tcmb+tr/main+menu/temel+faaliyetler/para+politikasi/para+politikasi+cerceve.
27. Menderes Çınar, “Turkey’s Transformation under the AK Party Rule,” The Muslim World, Vol. 96, (2006), pp. 469-486.
28. Ünay, “Economic Diplomacy for Competitiveness,” pp. 21-47.
29. Hakan Yavuz, Secularism and Muslim Democracy in Turkey, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2009).
30. “Yürürlükte Bulunan STA’lar,” Republic of Turkey Ministry of Trade, retrieved February 10, 2021, from https://ticaret.gov.tr/dis-iliskiler/serbest-ticaret-anlasmalari/yururlukte-bulunan-stalar#:~:text=22%20STA’m%C4%B1z%20ise%20(EFTA,ve%20Birle%C5%9Fik%20Krall%C4%B1k)%20h%C3%A2lihaz%C4%B1rda%20y%C3%BCr%C3%BCrl%C3%BCktedir.
31. “World Economic Outlook: Growth Slowdown, Precarious Recovery,” International Monetary Fund, (2019).
32. “Turkey Government Debt to GDP,” Trading Economics, retrieved February 10, 2021, from https://tradingeconomics.com/turkey/government-debt-to-gdp.
33. “Turkey Central Government Budget,” Trading Economics, retrieved February 10, 2021, from https://tradingeconomics.com/turkey/government-budget.
34. “Turkey’s Top Export Countries,” Doing Business in Turkey, (January 28, 2019), retrieved from https://doingbusinessinturkey.com/turkeys-top-export-countries/.
35. “Labor Force Statistics,” Turkstat, (February 10, 2021), retrieved from https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Labour-Force-Statistics-November-2020-37480.
36. “Free Trade Agreements,” Republic of Turkey Ministry of Trade, retrieved January 3, 2021, from https://www.trade.gov.tr/free-trade-agreements#:~:text=Under%20the%20Customs%20Union%2C%20Turkey,the%20EU’s%20Common%20Commercial%20Policy.&text=Turkey%2C%20in%20line%20with%20the,in%20parallel%20with%20the%20EU.
37. “Free Trade Agreements.”
38. “Free Trade Agreements.”
39. “EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement: Council Adopts Decision on the Signing,” European Council, (December 29, 2020), retrieved from https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2020/12/29/eu-uk-trade-and-cooperation-agreement-council-adopts-decision-on-the-signing/.
40. “Eastern Mediterranean: Turkey Must Immediately End Illegal Drilling Activities,” Europäisches Parlament, (September 17, 2020), retrieved from https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/de/press-room/20200910IPR86828/eastern-mediterranean-turkey-must-immediately-end-illegal-drilling-activities.
41. “List of Importing Markets for a Product Exported by United Kingdom,” International Trade Centre, (September 17, 2020), retrieved from https://www.trademap.org/Country_SelProductCountry_TS.aspx?nvpm=1%7c826%7c%7c%7c%7cTOTAL%7c%7c%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c2%7c2%7c1%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1.
42. “UK Total Trade: All Countries, Non-seasonally Adjusted” Office for National Statistics, retrieved February 10, 2021, from https://www.ons.gov.uk/businessindustryandtrade/internationaltrade/datasets/uktotaltradeallcountriesnonseasonallyadjusted.
43. “Turkey: Foreign Investment,” Santander, retrieved December 27, 2020, fromhttps://santandertrade.com/en/portal/establish-overseas/turkey/foreign-investment.
44. “Continuing the United Kingdom’s Trade Relationship with the Republic of Turkey,” Department for International Trade.
45. “FDI in Turkey,” The Investment Office of the Presidency of the Republic of Turkey, retrieved fromhttps://www.invest.gov.tr/en/whyturkey/pages/fdi-in-turkey.aspx.
46. “FDI in Turkey,” The Investment Office of the Presidency of the Republic of Turkey, retrieved fromhttps://www.invest.gov.tr/en/whyturkey/pages/fdi-in-turkey.aspx.
47. “Continuing the United Kingdom’s Trade Relationship with the Republic of Turkey,” Department for International Trade, retrieved January 6, 2021, from https://assets.publishing.service.gov.U.K./government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/948936/ccs1220781734-turkey-trade-pr-accessible.pdf.


